
According to the requirements of GOST 5686 “Soils. Methods of field testing of piles", SNiP 2.02.03-85 "Pile foundations", SP 50-102-2003 "Design and installation pile foundations", "Pile testing programs", pile testing is carried out using two main methods:
our company conducts both types tests, although the latter are much cheaper and technically simpler. It is worth noting, however, that testing piles using the second method is not used on plastic clay soils, as well as on bulk soils in the form of construction waste or household landfills.
Transmission of shock and longitudinal waves. Analysis of villi using the wave equation. Some aspects of determining the volume of piles using the wave equation. The volume of piles depending on time in clayey and sandy soils. Dynamic system of pile soil with variable attenuation.
Soil attenuation in saturated sandy soils to determine pile capacity using the wave equation method. Soil attenuation in the analysis of wave equations of a piled tank. Energy-impedance-energy relationship for driven piles. Time-dependent capacity of piles in clay soils using dynamic methods.
Field tests of piles are carried out:
Thus, the compliance of the load-bearing capacity of the piles with the calculated design loads is checked.
Limitations of guideline formulas for predicting the bearing capacity of piles in sand. Research on the correlation of wave equations. Real and apparent relaxation of driven piles. Effect of time and supported load on ultimate capacity of piles in hard clay.
Design of pile foundations. Analysis of wave equations for driving piles using personal computers and programmable calculators. Relaxation of piles in sand and inorganic silt. Rice. 4 The Smith variable decays in clay and unsaturated sand, after Swinkin.

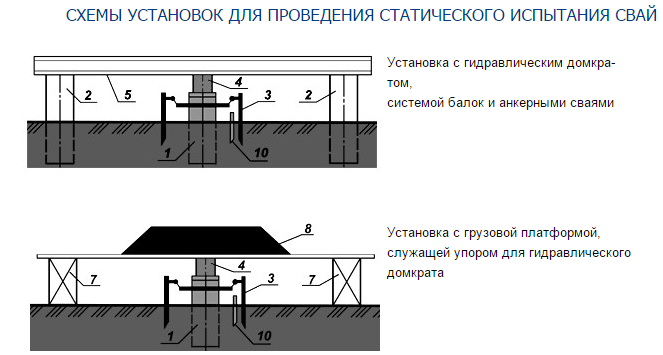
To carry out static tests of piles for pressing and pulling loads, a special installation is required, which consists of:
See also:
Rice. 5 Change in Smith attenuation in saturated sand, after Swinkin. Deep bases are those where the depth of the base is usually greater than twice the width of the base. Deep foundations are required for various reasons. about why deep foundations and types of deep foundations are needed.
While the composition and depth of the bearing layer for shallow foundations may vary from one site to another, most pile foundations locally encounter similar deposits. Since pile capacity based on soil parameters is not as reliable for load testing, the first step is to obtain full information about the type, size, length and capacity of piles commonly used in the area. The correlation of soil characteristics and associated load tests is essential in order to determine the type of soil tests that should be preformed and to make a reasonable recommendation for the type, size, length and capacity of the pile, since most formulas are empirical.
Static test process for piles

When testing a pile using the static method, it is loaded in steps, the weight of which is calculated depending on the design load on the pile (usually no more than 1/10). In this case, the load in the next stage is carried out after the settlement at the previous stage has stabilized.
If information about the piles in locality not accessible or reliable, a test pile may need to be carried out and correlated with soil data. A standard penetration test to determine cohesion is to determine the friction angle for each layer of soil cohesion, less soil soil.
Impenetrable blade shear test clay soils. In the case of tow piles prescribed for hard clays, it is also necessary to check with and from remodeled samples. Dry shear strength parameters are also determined to represent the in situ soil condition at the end of the construction phase.
Before loading the pile under test on all measuring instruments the zero mark is set. Readings are also taken from all instruments at each loading stage.
Conditional stabilization of the pile is determined by the following criterion: at a given loading stage, the settlement rate of the pile does not exceed 0.1 mm. During the last 30 minutes of observation. 
Testing a self-tapping pressure meter to determine the subclass response modulus for horizontal deflection for granular soils, very stiff cohesive soils, soft rock, and weathered or jointed rock. Groundwater conditions and soil permeability influence which type of pile to recommend. Therefore, the level at which water remains in the wellbore is marked in the wellbore. Because the permeability of clay is very low, it takes several days for the water in the drill hole to rise to the groundwater level.
The value of the partial ultimate resistance is considered to be the load at which further loading of the pile is stopped.
We produce using any method. As we have already mentioned, the price for static tests is much higher, and they also require additional equipment. However, as mentioned above, in some cases it is simply impossible to do without static tests.
Groundwater samples should be tested to consider possible chemical effects on the concrete and reinforcement. The cone penetration test result for the same soil shows significant variation. Therefore, they need to be checked using additional information from other reconnaissance methods.
If the soil is not isotropic, then the same value cannot be assumed for the vertical direction. Dynamic load test is fast, reliable and cost effective effective method assessment of the bearing capacity of the pile. The dynamic load test involves a significant drum mass being applied to the top of the pile and causing it to experience at least a small amount of permanent lift. Accelerometers and strain transducers attached to the magnitude of the force and velocity of the pile when the free fall weight reaches the top of the piles.
The static testing technology (pictured below) shows the actual state of the permissible loads on the tested piles.
The test method is quite simple, but requires labor, time and special equipment. The principle is simple - you need to press on the pile under test with sufficient force so that it settles down. In this case, it is necessary to press, and not to drop something from above, as in dynamic tests. In this case, special stands are made above the pile being tested.
With our team of experienced engineers, we also work in the field of dynamic measurement and analysis. During the installation of production piles, he ensures that driving occurs according to the established criterion. It provides information about soil resistance during monitoring and driving efficiency. If damage is imminent, it shows a warning early enough to save the heap from total destruction. Monitoring occurs while driving in real time, without slowing down construction.
Stand for static testing of piles and soils
Such piles are called anchor piles. Installed on top of anchor piles metal beam, welded to them. It is against this obstacle that a hydraulic jack with a pressure gauge will be placed.
The test involves generating stress waves at the pile head and recording the reflected wave response. Analysis of recorded data can provide important information about the integrity of the existing pile. Dynamic load testing is a rapid method of assessing the bearing capacity of a pile for loads similar to the design loads. It can be used for precast piles, cast-in-place piles, steel piles or wood piles.
The generated compression waves travel down the stack and are reflected upward from the sock stack. The reaction of the reflected waves is captured by sensors located on the head of the piles. The reflected waves contain information about shaft friction, toe resistance and pile defects.
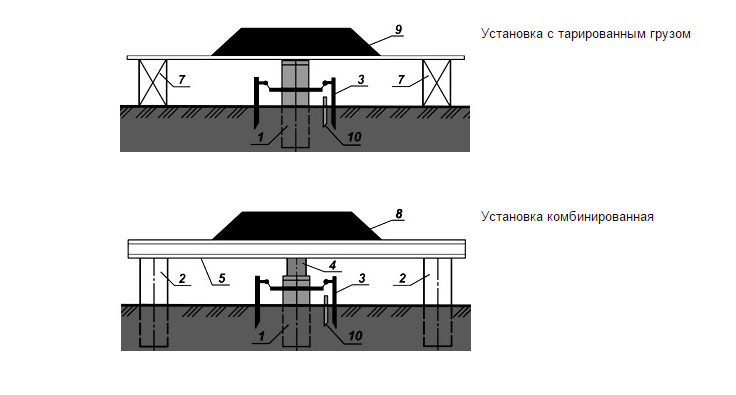
The test pile is driven slightly below the anchor piles for mounting a jack on it. The pressure is applied gradually in stages under constant monitoring. Testing is stopped either according to pressure gauge readings (usually 20-30% more than the planned load), or if the pile cannot withstand the load and sinks down. Static tests are more expensive, they take about a day, but they are the most accurate among all similar tests. According to SNiP, up to 1% of the total number of installed piles are subjected to static tests.
It is often possible to conduct several dynamic load tests in one day. The dynamic load test involves a significant mass of the drum being applied to top part foundation and causes her to experience a small constant set.
Accelerometers and strain transducers attached to the foundation measure the force and speed when the weight is dropped on it. What type of test do you want to perform? Fast load test. An important prerequisite for planning and constructing quarries or excavation foundations is knowledge of the upcoming site. For this purpose, ground investigations must be carried out, the nature and extent of which are determined by the complexity of the structure and the expected ground conditions.
To calculate the cost, an estimate is used and upon completion of the tests, a test report is issued.
The current testing standard is GOST 5682 2012. The standard applies to methods of field testing of soil with piles (reference, full-scale, probe piles), which are carried out during engineering surveys during the construction period. It also covers proof testing of various piles.
Based on the research results, a launch concept has been developed, which contains instructions and characteristic values for foundation dimensions. The purpose of these recommendations is to ensure substrate safety and ease of use, as well as cost-effective start-up.
In addition to geologic maps, geotechnical site investigation procedures provide information about local soil conditions. For this purpose, ground-based research is carried out. Their nature and extent depend on the complexity of the structure and the expected ground conditions. Geotechnical category 1 contains simple designs on level, stable ground that does not affect environment or groundwater. Geotechnical category 2 includes construction projects, which fall into neither category 1 nor category 3. Geotechnical category 3 includes construction projects with complex structures and challenging soil conditions that require advanced geotechnical knowledge. The civil survey engineer must determine an examination program to evaluate ground conditions based on the results.
Construction rules and regulations SP No. 50-¬102-¬2003, SNiP No. 2.02.03-¬85 apply to foundation inspection, foundation inspection and design of pile foundations for reconstructed and erected buildings and structures.
Dynamic tests of bored piles are carried out to determine the load-bearing and indentation capacity of the presented reinforced concrete products.
Geotechnical methods such as drilling, probing and excavation are carried out to investigate the site on site. In addition, geological maps and field surveys allow statements to be made on the ground. Allowable subsoil loads are determined by sounding results and our regional geological knowledge, and expected calculations are calculated by calculation. Here the statements are at the or level.
Depending on the results of the site survey, he recommends an individual launch concept and provides guidelines and characteristic values for foundation dimensions. The purpose of these recommendations is to ensure that the foundation is selected and specified in such a way that its failure can be excluded with a certain degree of confidence that the suitability for use is sufficient and that the initial measure is economical.
The technology used to test the indentation capacity and load-bearing characteristics is regulated by separate provisions of SNiP and GOST 5686-94.
To make an accurate assessment of the pressing ability of products, an oscillographic packing analyzer is actively used.
After this, data on the indentation and static load experienced by the piles, in accordance with the requirements of SNiP and GOST 5686-94, are recorded in the relevant documentation. Data regarding soil characteristics is also entered there.
In addition to the general assessment of soil conditions in relation to the bearing capacity of the foundation, especially in the construction of industrial and commercial buildings, the floor slab and traffic zones must be considered. The floor layer must be installed under the floor slab, which must be suitable for the intended use in terms of thickness and material composition for technical reasons as well as cost reasons. In addition to ground conditions, vehicles provided in the hall, such as forklifts, trucks which must be taken into account.
Dynamic tests for bored piles, as well as assessment of their pressing capacity, are carried out with an orientation towards any type of soil into which driving will be carried out.
Regardless of the series characteristic features soils into which the presented bored reinforced concrete products will be driven, all work is carried out with a clear focus on the requirements of GOST and SNiP.
In addition, it is also necessary to check whether the installation of machines or racks, in extreme cases even high-level storage, will result in special requirements for the base layer and substrate. As a result of surface loads having large drops in influence, installing a simple base layer is often insufficient under floor slabs and more extensive soil improvement measures will be required in this case.
Already for the production of a simple load-bearing layer, it is necessary to check whether the grounding plan, consisting mainly of cohesive soils, has sufficient load-bearing capacity. The same applies to the increased installation requirements of machines and high stand bearings. In this case, a reinforced support layer must be provided and, if necessary, an improvement in floor depth can be provided.
Dynamic and static testing of piles, as well as soil testing, is carried out during the construction of such objects as:

These piles are used for test driving. In this case, the loading device located above the piles is a special hydraulic hammer of the falling or impact type.
If there is no such unit at the construction site with which work on piles is carried out, then the estimate implies the presence of an alternative device for driving.
In this case, the test program for bored reinforced concrete products allows the use of a self-made tubular type hammer.
Based on the requirements of GOST and SNiP, the weight of this hammer for bored piles is 3.2 tons. Its installation is made from elements located between the piles.
Assembly is carried out in accordance with GOST and SNiP regulations, installation is carried out using a crane, in the space between the piles, in the place where soil tests will be carried out in the future.
Dynamic tests of piles are carried out in accordance with the requirements of GOST and SNiP at certain stages of work, the estimate is approved in advance. So, tests of bored piles are carried out:

As a result, a dynamic load test report is drawn up for the piles. It is worth noting that dynamic and static tests of bored products and soil studies are carried out:
GOST and SNiP allow the use of the same equipment during testing as during driving; these provisions clearly indicate the required distance between piles during work.
The final result of testing bored products is presented in the form of the resulting pile failure value. This is the depth to which the pile is immersed with one hammer blow.
All current measurements of bored piles are carried out using special device– failure meter. When taking measurements, the accuracy parameter of such a device is 1 mm.
This device, with appropriate settings, can make accurate measurements of the distance between piles. All stages of the measuring work are carried out in accordance with the requirements of SNiP.

The dynamic testing method has a number of irrefutable advantages over the static method. When implementing this method, a high degree of mobility is available, it is quite economical and is applicable to all types of currently existing piles.
The presented method provides a real opportunity to significantly increase the load-bearing capacity of the product. All this is done in accordance with the provisions of SNiP.
Such an increase in the parameter is possible if the pile, during driving, is immersed with its tip into a weak layer, which has greater compressibility.
In clay-type soils, which are distinguished by their homogeneity within the area of the building’s foundation, when piles are driven to the same depth, the magnitude of failures may vary.
Coupled with the short immersion interval, the data provided can be misleading, and therefore an opinion may be formed based on different values of the load-bearing capacity of the products.
In this case, it is recommended to carefully compare the results obtained with those obtained during static surveys. In the process one thing will emerge general meaning the level of resistance of the presented reinforced concrete products.
In most cases, dynamic testing is initiated three times. The first time, all actions are performed on existing products that are selected for work and construction. This happens before action begins with the pile foundation project.
![]()
In the process, an indicator of the level of heterogeneity of soil deposits in the place where construction will take place is determined.
The next stage after this is carried out immediately at the moment of driving. In the process, the load-bearing qualities of the product are assessed and the properties of load-bearing soil layers and weakened areas are studied.
After completion of work it is carried out The final stage tests. It provides the most reliable data on load-bearing capacity after they have been in the ground for some time.
When driving, in the process of monitoring current changes in failures, it is possible to identify those soil layers that are load-bearing.
This also allows for a comparative assessment of the load-bearing capacity parameters of already clogged products in order to identify possible weakened areas.
In clay-type layers, test driving is carried out using a hammer, which carries out a short series of blows. This allows you to keep the soil structure intact.
All current dynamic tests are carried out with the assistance of the equipment and machinery that was used in performing the main range of work.
Upon completion, the failure value becomes available. It is equal to the degree of immersion of the product into the ground after one blow with a hammer is made on it.

The accuracy of the data that will be obtained directly correlates with the height of the hammer and the specific gravity of its striking part.
This also includes the weight parameters of the pile and its cap. Some attention is paid to the level of accuracy of measurements taken during elastic movements of the product in the ground after an impact.
During the construction of a building and its subsequent commissioning, sandy and clayey soils are subject to compaction as a result of the static load affecting them.
Soil testing has a very serious impact on the entire process of building construction. This is due to the fact that the strength and stability characteristics of the entire structure under construction directly depend on the parameters of the bearing capacity of the soil.
This procedure is performed in order to study in detail physical and mechanical characteristics soils, determine the features of their geological structure and identify the conditions that affect the balance of the entire soil mass in a given area. In most cases, two mandatory stages of this type of testing are carried out.

Laboratory tests make it possible to determine the necessary parameters of the physical and mechanical qualities of soils, and field tests reveal the level of soil resistance in its natural conditions.
The work carried out helps to create the most optimal work schedule and predict the degree of sustainability of the future building.
In addition, this facilitates the selection of the most effective way aimed at strengthening the foundation. These procedures are also carried out in order to avoid the collapse of erected buildings.
Tests can be carried out not only in open construction sites, but even during the study the foundation is already ready. If construction is carried out on an old foundation, then the soil must undergo a mandatory study procedure.
When choosing the equipment that is necessary for correct tests of this kind, the orientation is carried out on the features of the method by which the immersion will be carried out. Currently, the following methods are actively used:

Static testing of piles begins with the identification of the number of existing products and the places where they will be driven further.
After this, the test samples are immersed reinforced concrete structures. All ongoing testing work is carried out with the participation of those structures that lie in areas with the worst ground conditions.
All test work begins by waiting for a period of “rest” for the pile. Those structures that will be immersed using other methods are brought into readiness no earlier than one day before the start of the process.
All work begins only after the product made of concrete hardens to 80% of its strength. All work is carried out evenly without impact and in compliance with the load on the structure. The procedure is established in advance and is displayed in the test program.
When deepening the lower ends of the structure into clastic-type soils, it is allowed to achieve three stages (levels) of load, which amount to 1/5 of all combined loads.
The first test pile must have high strength, due to this it can be ensured that all required characteristics. If necessary, the pile is reinforced by connecting an external ring.
There are no similar entries.