
Flat roofs are in demand in modular construction. Among the advantages of this method are the affordable cost and high speed of construction of housing, as well as the possibility of gradually increasing its area
Architects and developers are attracted to these unusual buildings, on which you can equip an observation deck or even set up a real hanging garden. Of course, in practice everything turns out to be more complicated than in theory.
Designing a flat roof raises many questions regarding its cost, choice of materials for insulation and waterproofing, organization of water flow, maintenance, etc. Finding answers to them is not so easy. The fact is that domestic contracting companies working in the field of cottage and rooftops are well familiar with the most popular design - pitched, but, as a rule, they have no experience in constructing flat roofs, which are designed completely differently.

What immediately attracts attention is the fact that the area of a flat roof is smaller than a pitched roof, which means that less materials will be required, and the work will be cheaper. However, this statement is only true for regions with a warm climate and low snow load, especially if we are talking about an unused roof. IN middle lane In Russia, to ensure the reliability and durability of a horizontal roof, it is necessary to apply rather expensive engineering solutions.
Beam floor
In principle, when constructing a floor, you can use a combination of beams (wooden, steel) and load-bearing corrugated sheeting. However, experts do not recommend using wooden beams (with the exception of those made of LVL beams with a cross-section of 200 × 100 mm) in regions where the snow pressure exceeds 1.2 kPa (about 120 kgf/m2) - that is, in most of the territory of the Russian Federation. A roof covering made of steel I-beams and corrugated sheets with a wave height of 60 mm and a wall thickness of 0.7 mm allows you to cover a span of up to 12 m and can withstand a pressure of at least 6 kPa. But in general, it is less durable than concrete, and is relatively rarely used in individual construction. It makes more sense to use corrugated sheeting as permanent formwork, which, by the way, does not replace the need to build a reinforcement frame.

It turns out that 1 m2 of a flat concrete or steel base, the load-bearing capacity of which will allow it to withstand the weight of snow cover, costs 2–2.5 times more than a wooden beam structure of a pitched roof. The difference in the volumetric consumption of insulation is leveled due to the fact that a flat roof requires more expensive high-density material. There is still hope to save on roofing, but modern polymer membranes - the optimal waterproofing for horizontal roofs - are no cheaper (and sometimes much more expensive) than flexible tiles. There is no need to install snow guards, but you cannot do without a roof hatch and a drainage system. If you try to cut costs according to the estimate, you will subsequently have to pay the price of having to repair the roof every 10–15 years.
Finally, it should be taken into account that flat roofs are appropriate only on houses of modern architecture - with a large glazing area and complex finishing with the latest facade materials. Both will not be cheap at all.

As a rule, in low-rise housing construction, the flat roofing is a prefabricated or monolithic reinforced concrete slab. Reinforced concrete slabs (PB, hollow PC, PV, etc.) are capable of covering a span of up to 9 m in length and can withstand a pressure of 8, 9 or 12.5 kPa (this value is indicated by the last digit in the product labeling). They can serve as a “base” for any roofing pies, including top layer from paving slabs or fertile soil. However, to install the structure, it will be necessary to ensure that a truck crane can enter the site (while steel beams and flooring can be easily lifted using winches). The depth of support of the ceiling on the wall depends on the material of the latter - for example, for brick this parameter should be equal to the thickness of the slab. Before proceeding with the installation of the roof, it is important to seal the joints of the elements with mortar and additionally seal them with elastic polymer tape.

The main advantage of membranes based on artificial rubber is that they retain elasticity at low temperatures, that is, they can be installed in winter
Classification of flat roofs
Flat roofs are divided into unused and used. The former visit only for inspection, prevention and repair; For this purpose, a roof hatch is installed, to which an attic ladder leads. The roof in use in cottages most often serves as a terrace, that is, a durable wear-resistant coating must be laid on it, and the load-bearing base is designed for increased loads. A type of exploitation is a roof with landscaping, laid with a turf layer on top of the main heat-waterproofing pie; Usually there are paths and a recreation area on it. A convenient exit to the roof in use should be provided, for example from a vestibule superstructure.
A monolithic reinforced concrete floor is erected from heavy concrete using removable (for example, from OSB boards on jack stands) or permanent (from corrugated sheeting) formwork. It is reinforced with a two- or four-level welded frame made of rods with a diameter of 12 mm. Dimensions monolithic slab are not regulated (unlike prefabricated), which provides the architect with freedom when designing a building; other advantages are the absence of seams, the comparative simplicity of the installation of passage units (chimney, ventilation ducts) and high load-bearing capacity (subject to compliance with technological regulations).

In the low-rise sector, mostly flat roofs without attics are in demand, because the attic requires additional costs and disrupts the architectural proportions of the house. This means that the roof must protect against winter cold and summer heat. A common feature of flat roofs is that the heat-insulating layer is located on top of the supporting structure (in pitched roofs it is usually located between the rafters). If you insulate the room from below, the dew point may shift into the thickness of the ceiling, which will lead to a reduction in the service life of the latter.

Mastics should be used primarily on roofs of complex configurations
As for roofing options, there are dozens of them. Suffice it to say that more than 40 “recipes” are given in SP 17.13330.2011 alone. At the same time, companies producing coatings and insulation materials are offering more and more new engineering solutions. However, they are always based on one of two circuit diagrams- traditional or inversion.

“TN-ROOF Terrace”: 1 - ceiling; 2 - vapor barrier; 3–5 - EPPS (including the slope-forming layer); 6 - fiberglass; 7 - LOGICROOF V-GR membrane; 8 - geotextile; 9 - tiles on supports
The traditional design in general terms is as follows: a vapor barrier film (polypropylene, polyethylene, butumen-polymer) is laid on top of the load-bearing base, followed by insulation, for example, slabs of mineral wool, having a compressive strength at ten percent deformation of at least 30 kPa, in one or two layers with a total thickness of 200 mm. Above is a separating layer (for example, made of polyethylene film), along which a reinforced slope-forming screed is poured (a flat roof must be given a slope of 2-3% towards the center or edges to ensure water drainage). The dried screed serves as the basis for a roll or mastic waterproofing coating.
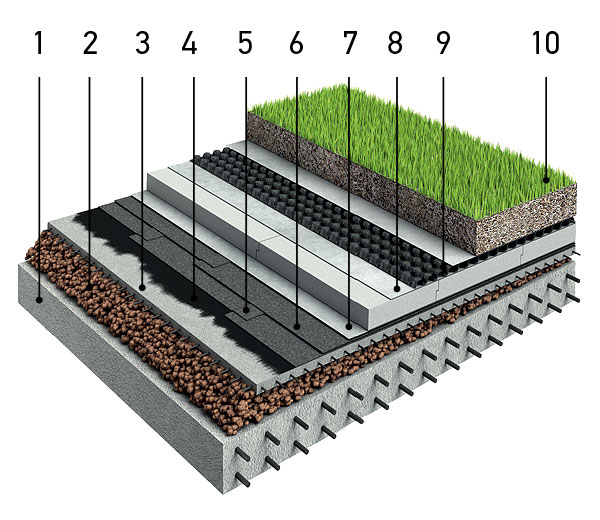
“TN-ROOF Green”: 1 - overlap; 2 - ramp made of expanded clay; 3 - reinforced screed; 4 - bitumen primer; 5 - “Technoelast EPP”; 6 - “Technoelast Green”; 7 - geotextile; 8 - EPPS; 9 - PLANTER membrane GEO; 10 - fertile layer
Other options are also possible. For example, a slope-forming screed can be located at the very bottom of the pie; in this case, the roof waterproofing is fixed with gravel ballast, paving slabs on supports or special dowels. Some materials, say the “RUF SLOPE” system (Rockwool) or “TechnoNIKOL Slope”, allow you to do without a screed altogether: the slabs have variable thickness, and with their help it is not difficult to create smooth changes in level to ensure water drainage.
An inversion roof is designed differently: in it, insulation resistant to constant exposure to water (usually extruded polystyrene foam - EPS) is located on top of the waterproofing. At the same time, the latter is reliably protected from mechanical damage and is located in the positive temperature zone (freezing-thawing cycles are destructive for almost any material). Inversion roofing It’s easy to turn it into a usable one, for example, by filling the insulation with a drainage layer of sand and gravel and laying paving slabs. The disadvantages of the design include more complex drainage. However, we need to talk about gutters separately.
There are special requirements for thermal insulation for flat roofs. The material must not only have a low thermal conductivity coefficient, but also have good resistance to mechanical loads - both distributed (pressure from the overlying layers of the roofing pie, equipment, snow) and local ones that arise during installation. In addition, it is important that the material has hydrophobic properties and is non-flammable. At the moment, there are several ways to install thermal insulation: using mechanical fasteners, adhesive and free laying. In addition to traditional two-layer insulation, single-layer installation is becoming an increasingly popular solution. Rockwool offers unique dual-density slabs that consist of a rigid top layer and a lightweight bottom layer, which speeds up work and improves its quality.
Grigory Gromakov
Specialist in development of the “Flat roofing” direction of the ROCKWOOL company
The flat roof is equipped with a parapet (attic) 30–90 cm high, which helps ensure an organized roof; on a roof in use it also serves as a safety fence. At the same time, the design of gutters should be approached very responsibly, because in case of an error, a huge puddle can form above your head, which can also lead to damage to supporting structures.
As a rule, the choice is made in favor internal drain. Such a system is less exposed to the atmosphere and is therefore more durable and reliable than an external one. Let's talk in more detail about its main elements.
Water intake funnels are installed on low areas of the roof. As a rule, on roofs with an area of up to 150 m2, two funnels are installed - the main one, connected to the riser, and the emergency one - with water discharged through a hole in the parapet. With an increase in the number of funnels and risers, the reliability of the system increases, but its cost also increases.
For inversion and green roofs, special funnels with drainage rings have been developed to collect moisture from the intermediate layers. Water receivers must be equipped with electric heating based on a self-regulating cable - then they will properly perform their function during alternating thaws and frosts.

Traditional covering with external drainage 1 - ceiling; 2 - slope-forming screed; 3 - vapor barrier; 4, 5 - mineral wool insulation; 6 - waterproofing; 7 - drain
In a new type of system, the so-called siphon-vacuum system, special funnels are used to prevent air from being sucked into the water flow. Thanks to them, the speed of fluid movement in the pipe (and hence the throughput of the latter) increases, which makes it possible to reduce the diameter of the system elements. However, for low-rise buildings, the savings turn out to be insignificant; moreover, such systems require more accurate calculations than gravity systems.
The drainpipe is made from sewer pipes - polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride, and it makes sense to use sound-absorbing products, for example RAUPIANO Plus (REHAU), or soundproof the riser, otherwise you will hear the murmur of water for hours. The riser is connected to the funnel using an elastic coupling. When laying pipes, the number of bends and the length of horizontal sections that reduce throughput systems.
A drainage pipe, laid in a basement or insulated underground, connects the riser to a rain drain or provides water discharge into a tray linear drainage. In the second case, there is a risk of clogging the outlet with ice, so the riser should be equipped with a “winter” outlet to the domestic sewer (the latter should be equipped with a water seal). The outlet pipe is cleaned through a collapsible connection or an inspection module.

Drawing: Vladimir Grigoriev/Burda Media
Inversion roof covering with internal drainage 1 - screed; 2 - PVC membrane; 3 - EPPS; 4 - funnel with drainage ring; 5 - drainage membrane; 6 - sand; 7 - paving slabs
When choosing the standard size of elements of a traditional gravity system, they proceed from the intensity of rain in a given area, focusing on SP 32.13330.2012.
The external drainage system is more vulnerable than the internal one, and also affects the appearance of the facades, but it does not require holes in the roof and ceilings and does not eat up the usable area of the house. Water is discharged through parapet funnels or pipes embedded in the parapet, under which classic funnels (like on a pitched roof) and down pipes attached to the walls with brackets are installed. When calculating, it is assumed that for every square meter of roof area there should be 1–1.5 cm2 of the cross-section of drainpipes. Elements outdoor system can be made of PVC, steel, copper, zinc-titanium.
For roofs in use, as well as roofs installed in regions with harsh climatic conditions, the inversion scheme is ideal. Because the waterproofing layer located under thermal insulation, it is protected from mechanical influences, as well as from temperature changes and UV radiation, which significantly extends its service life roofing system. Waterproofing materials based on modified bitumen must be laid in at least two layers - this technology is more common, and in addition, it allows you to level out possible errors when fusing the material. One layer is enough for a polymer membrane, and reliability is ensured by automatic welding equipment, which greatly increases the speed of work. In addition, when installing a polymer membrane, an open flame is not used, so the technology is considered safer.
Dmitry Mikhailidi
Head of the Engineering and Technical Center of the Technical Directorate of the TechnoNIKOL Corporation
Since ancient times, turf-covered roofs have been used in countries with moderately cold and humid climates, and the green carpet performed the main moisture-protective function in them.
As part of the modern concept of a green roof, a layer of fertile soil with plants is needed to give unusual features to the appearance of the building, decorate the terrace roof and extend the service life of the coating by covering it from ultraviolet rays. In addition, it absorbs rainwater, unloading the gutters, dampens the sound of rain, protects the rooms on the upper floor from overheating in the summer and reduces heat loss in the winter. It is believed that landscaping almost doubles the life of a roof. Its disadvantages include an increase in loads on the supporting structures of the building and an increase in construction costs. In addition, a green carpet needs care, the intensity of which depends on the selected plant species. If you do not pay due attention to the plants, they will freeze and die from drought.
To green the roof, you should lay on top of the main waterproofing layer (in an inversion scheme - on top of the insulation) an additional cake made of materials that will ensure protection of the waterproofing layer from roots, filtration and drainage of rainwater. For these purposes, special films, dense geotextiles, gravel bedding or drainage and moisture storage membranes made of high-density polyethylene, for example PLANTER GEO or Delta-Floraxx, are used.
Then a mixture of minerals and fertilizers is poured - the so-called soil substrate. You can prepare it yourself by adding fine expanded clay (5–15%), sand (about 20%) and fertilizers to a light soil mixture of neutral peat. As for plants, the easiest way is to limit yourself to meadow forbs and drought-resistant ground covers - sedum, herbaceous carnation, thyme. They do not need to organize an irrigation system, and the thickness of the soil layer can be only 6–12 cm (this type of roof is called extensive). If you plan to walk along the roof among ornamental shrubs, you will have to provide watering and increase the soil thickness to 20–40 cm. Such a roof is called intensive; it creates a significant additional load on the floor, so it must be provided for at the design stage of the building.

Rolled materials based on modified bitumen, as a rule, are fused with a gas burner, but it is difficult to prevent small flaws that can cause leakage (if there is no second layer)
Rolled PVC membranes , for example, Sikaplan WP, Logicroof, Ecoplast are strong and durable (up to 30 years without repair) and do not support combustion. However, they require a professional approach to installation (the joints of the strips must be carefully welded with hot air) and are relatively expensive - from 320 rubles. for 1 m2. It is important to consider that this material does not tolerate contact with bitumen.
Rolled membranes made of ethylene-propylene rubber (EPDM) and thermoplastic polyolefins (TPO) , for example Firestone RubberGard, Logicroof P-RP, retain elasticity at low temperatures. Note that EPDM membranes are highly flammable (class G4) and are designed mainly for use in the construction of an in-use roof, where the waterproofing is covered with tiles, gravel or soil. EPDM and TPO membranes cost 1.3–1.5 times more than polyvinyl chloride membranes (mostly imported products).
Polymer-bitumen mastics They allow you to create a seamless coating, but they can only be applied to a durable, non-cracking base - a floor slab or a carefully reinforced screed, and this process is quite long and labor-intensive. The service life of a two-layer coating with a thickness of 5 mm is about 20 years, the price is from 120 rubles. for 1 m2. In practice, mastics are used mainly for roof repairs and gluing rolled materials.
Polymer and cement-polymer self-leveling waterproofing
, say Aquascud, Osmolastic, Osmoflex, is highly elastic
and UV resistance. To improve performance, materials are used in combination with special primers and lining films, and reinforced with mineral fiber (all components are supplied as a single system). The estimated service life of the coating is more than 50 years; price - from 700 rub. for 1 m2.
| Advantages | Flaws |
|---|---|
| Eliminates snow avalanches and reduces the risk of falling ice. | Requires significant costs to construct a foundation with high load-bearing capacity. |
| Provides convenient access to chimneys, ventilation risers, antennas; Compared to pitched ones, it is easier to maintain and repair. | It is more susceptible to atmospheric factors than pitched, so durability is guaranteed only if expensive materials are used. |
| Can serve as a recreation area or terrace. | Requires increased attention to the arrangement and condition of the drainage system (especially with internal drainage). |
| Slightly less susceptible to wind loads than pitched. | |
| Allows you to implement the principle of phased modular construction (to make an extension to a house with a pitched roof, you need to solve a difficult architectural and design problem). |
Roof- this is the upper enclosing structure of the building, performing load-bearing, waterproofing and, with attic-free (combined) roofs and warm attics, thermal insulation functions. The roof is the upper element of the roof (covering) that protects buildings from all types of atmospheric influences. Roofs more than other elements of the house are exposed atmospheric influences, and the costs of their maintenance and repair significantly affect the cost of operating the entire house. Therefore, roof structures must have strength and durability corresponding to the class of the building. The shape of roofs is one of the essential parameters, which is dictated not only by fashion, but also by many practical considerations, including ease of use, safety parameters, and expansion of the useful areas of the building. Indeed, in addition to the constant load from its own weight, the roof structure must also withstand temporary loads: snow (in Ukraine from 800 to 1800 Pa); wind pressure and rarefaction - on the windward and leeward sides, respectively. In addition, the roof must withstand the loads that arise during operation, while the shape of the roof should not complicate, increase the cost and, moreover, reduce the efficiency of operational maintenance - repairs, cleaning, etc. What shapes do roofs come in?
Basically, two are used type of roofs:
. pitched
. flat
In fact, to ensure the removal of precipitation, roofs are always made with a slope. The slope of roofs is indicated in degrees relative to the horizontal surface, for example 27°, 45° or as a percentage. Roofless roofing with a roof slope of up to 3-5% is called flat. Such roofs can be used for terraces, sports, playgrounds, gardens, in other words, a flat roof can be used.
The question of which roofs are better - pitched or flat - is not entirely correct. It is generally accepted that pitched roofs (also called inclined roofs) are more common in cottage construction. At the same time, flat roofs are more likely to belong to industrial public buildings and modern urban development. However, this is just a stereotype. In urban development and infrastructure buildings, pitched roofs (attic construction) are widely used, while in cottage construction - flat roofs, including those in use.
Pitched roofs usually consist of an upper part (shell) called the roof, a base (lath or sheathing) that directly supports the roof, and a supporting structure - rafters, which usually rest on the outer and interior walls. The roof has the shape of inclined planes - slopes. The magnitude of the slopes of the slopes depends on many factors, including the architectural composition of the building, the average amount of precipitation, temperature changes, the direction and strength of the wind, the roofing materials and even the architectural and natural surroundings of the building. So, for example, to reduce snow loads in areas with heavy snowfall, roofs with steep slopes are designed with a slope of more than 30°, for example 45°, at which the snow easily slides off the roof, and if it is small, it is blown away by the wind. But it should be taken into account that if trees grow close to the house (cottage development) or there are higher buildings around (city), protecting it from the wind, significant snow deposits will form on the roof. In other words, the question of the magnitude of the slope of the slopes should only be resolved comprehensively, taking into account many factors that need to be known and, moreover, be able to take into account.
Pitched roofs consist of the following elements:
. inclined planes - slopes;
. rafters - the basis for the slopes;
. lathing along the rafters - to distribute the load over them;
. Mauerlat - for supporting the lower ends of the rafter legs;
. inclined ribs - at the intersection of slopes;
. horizontal ribs - skates;
. valleys and grooves - at the intersection of slopes with incoming corners;
. eaves overhangs - the edges of the roof above the walls of the building;
. pediment overhangs - located obliquely;
. gutters - drainage elements for collecting water from slopes;
. water inlet funnels - for collecting water from gutters;
. drainpipes into which water flows from water inlet funnels.
The height of the attic is determined by the width of the house, the slope, and the roof structure. It should be taken into account that in the attic a passage with a height of at least 1.6 m should be provided along the entire room. This is a requirement fire safety. It is also important that the height of the attic in the lowest places is not less than 0.4 m - this will be required for inspection and, if necessary, repairs.
Flat roofs are widely used in the construction of multi-storey residential and public buildings, industrial and agricultural buildings. Flat roofs sometimes called roofless, as well as the “last”, attic floor they combine - there is even a special term - combined coatings. The paradox is that a roof without an attic may well have an attic, or rather - technical floor. In any case, in a flat roof the load-bearing structures (aka ceiling) last floor) and waterproofing carpet (roofing) are combined in them. Unlike pitched roofs, flat roofs do not use piece or sheet materials as roofing materials. Here, materials are needed that allow the construction of a continuous carpet (bitumen, bitumen-polymer and polymer materials, as well as mastics). This carpet must be elastic enough to withstand temperature and mechanical deformations of the roof base. The thermal insulation surface, load-bearing slabs, and screeds are used as the base.
It is generally accepted that a flat roof is more economical and cheaper than a pitched roof. There is a certain reason for these views.
. The area of a flat roof is less than the area of a pitched roof (if equal area buildings, of course), so the roofing materials used for a flat roof may turn out to be cheaper simply due to the required footage.
. The construction of a flat roof takes place in less “extreme” conditions, therefore, we can talk about simplifying the roofing works.
. At the same time, flat roof maintenance, preventive inspections, cleaning gutters, working with antennas, chimneys, ventilation ducts and the flooring itself is much simpler and does not require special knowledge from the operating personnel - they do not have to be part-time climbers.
. In addition, it is convenient to mount a variety of equipment on a flat roof, including, for example, climate control equipment - external air conditioning units, for example, which in the case of a pitched roof are placed on the facades.
. On the one hand, a flat roof experiences greater snow loads than a pitched roof (however, since there is no rafter system, this load is transferred directly to the ceiling), on the other hand, a flat roof does not have windage, unlike pitched roofs.
. Also usually indicate the possibility of deployment phased construction- with accommodation under temporary cover.
. You can use a flat roof as an exploitable one, either to compensate for the insufficient area of land (budget cottage construction or dense urban development), or to identify the aesthetic advantages of a flat roof (device winter gardens and outdoor gardens, playgrounds, garages, etc.)
Flat roofs nowadays are undeservedly forgotten and not spoiled by the attention of developers. In private housing construction, they are found mainly in the southern regions, where heavy rains and snowfalls are rare. Hip roofs, on the contrary, have become firmly established in the projects and minds of homeowners.
This state of affairs can be explained simply: until recently, builders did not have reliable and durable waterproofing.
Standard roofing felt - cardboard impregnated with bitumen - cannot resist moisture and temperature changes for long. Even a thick 4-layer coating from it has to be changed after 6-8 years.
Today, interest in flat roofs is beginning to grow.
There are several reasons for this:
Strictly speaking, you will not see a completely flat roof on a building. Any of them has minimum slope from 1 to 4% required for precipitation runoff.
There are four types of flat roofs:
Unused roofs are found on industrial buildings.

Operated roofs have found application in public and private construction. They are equipped with recreation areas, cafes and restaurants, and used as parking lots and helipads.

Green (lawn) coverings are made to decorate buildings, as well as when there is not enough space on the site. In addition to the aesthetic function, they perform an important practical task. A layer of plant turf is an excellent heat and sound insulator.

Combined roofs with a flat surface are the most common option. Comfortable relaxation in the fresh air surrounded by green grass and flowering plants everyone likes it.
According to the method of drainage, houses with a flat roof are divided into two types:

Internal drainage is cheaper than external drainage because it does not require a large number of gutters, pipes, funnels and high-rise work to install them. It is more difficult to execute. Errors in creating a slope and poor-quality sealing of joints lead to leaks and damage to the integrity of the protective layer of waterproofing.
In use flat coverings with internal drainage it is more profitable. In winter, icicles do not grow on the eaves of such a roof. Drainpipes pass inside the building and therefore do not freeze. Cleaning debris funnels is easier and easier than hanging gutters.
According to the method of arrangement and arrangement of structural layers, experts distinguish two types of flat roofs:
The classic roofing “pie” is equipped using the following technology:

Classic flat roof structure
The main disadvantage of the traditional design is the vulnerability of the outer insulating layer from solar ultraviolet radiation and temperature changes.
Working to solve this problem, engineers came up with the idea of an inversion coating. In it, the main structural elements (insulation and waterproof membrane) are swapped. Waterproofing is hidden under polystyrene foam, which external influences protected by a gravel ballast layer or a tile finish.

Inversion coating design
The technology of work is changing accordingly. A waterproof carpet made of roofing felt or EPDM membrane is glued to the slab or spread on it, fixing it in places adjacent to the parapet.
The slope in this case is created in one of two ways:

Installing thermal insulation on a flat roof
Water intake funnels and pipes are installed at the lowest points of the slope. In addition to them, ventilation is installed to remove water vapor that accumulates in the area of contact between the vapor barrier and the insulation.

When arranging a covering designed for planting plants, the structure is supplemented with a top layer of waterproofing. Drainage layers of gravel are poured over it, geotextiles are laid and a fertile layer of soil is poured.
In addition to roofing coverings laid on reinforced concrete slabs, designs for houses with a flat roof on wooden beams have been developed.

Construction technology in this case may include the following operations:
There are many supporters of flat roofs among developers. They are attracted by the ease of construction, low cost of work and the possibility of placing a site for summer recreation.

A thick layer of snow on a flat roof is not a problem, but additional insulation
The design of buildings with such a roof fits perfectly into the style of minimalism, providing project developers with a wide field for creativity.

Spacious, comfortable and nothing superfluous is the motto of everyone who chooses a house with such a roof. A pitched roof visually weighs down the building, while a flat roof, on the contrary, makes it light and airy.

The appearance of the facade of a one-story house with a flat roof compares favorably with the rather boring variations of the “teremkovy” character.

On it, most often you will not see gutters and pipes, the water from which gets on the walls and spoils the appearance of the finish. Internal drainage is efficient, practical and invisible.
When starting the construction of a private house or cottage, every developer wants to know which roof is better and be confident in its reliability. One of the main factors that influence these parameters is the roof of the house, which must correspond to the design features and overall architecture of the building, as well as the material used for the roof.
The pitched roof of a house is the most common in the Russian region, because... The snow comes off well.
In the construction of private houses, various types of roofs are used, which differ in the number of slopes, their angle of inclination, and the possibility of installing an attic.
Advantages and disadvantages

There are a large number of different roof options that are used in modern low-rise construction. They have different configurations, their advantages and disadvantages, and the material used.
Flat roof. This design does not have any slope. It is practically not used in the construction of an individual house, since the flat surface retains precipitation on its plane. These factors cause the roof to quickly deteriorate, resulting in roof leaks.
Shed roof
In this option, it is assumed that one inclined surface (slope) will be installed over the entire area of the house. Such a roof rests on two load-bearing walls of different heights. This type is not particularly popular among private construction. Most often used in the construction of garages or utility rooms. By design they can be ventilated or non-ventilated. Ventilated roofs have a slope of 5-20 degrees, and unventilated roofs have a slope of 1-5 degrees.
Advantages pitched roof

Scheme for calculating the roof slope angle.
Disadvantages of a pitched roof
Gable roof
This option consists of two equal opposite slopes, one side of which rests on the load-bearing walls of the house, and the other two are connected at the ridge. The plane (wall) that is formed between two slopes is called a pediment. The pediment can be made either with an opening for a window, which is used to illuminate the attic space, or as a solid one. Beautiful attic windows make the entire building light and airy. This type of roof is the most popular and common in individual construction. As a rule, such roofs are made in houses that are not particularly architecturally sophisticated.
The gable roof has an attractive appearance and is very practical. Any material intended for this purpose can be used for the roof. Can give a home a sophisticated look decorative finishing pediments.
When building a gable roof, it is necessary to take into account its own weight structural elements, as well as additional load from snow and rainwater.
Advantages of a gable roof

Types of rafter systems for single-pitched and gable roofs.
Disadvantages of a gable roof
Hip roof
This type of roof consists of two slopes, which have a triangular shape, and two trapezoidal slopes. When constructing a hipped roof, there is no need to install gables. To illuminate the attic, attic windows are used, which are mounted directly on the roof slopes. Such a roof also has another name - hip, since the slopes triangular shape are called hips. If the roof consists of four equal slopes connecting at one point, then this type of roof is called a hip roof. Such roofs are most often installed in areas with a mild climate.
Advantages of a hipped roof
Disadvantages of a hipped roof

The envelope-shaped roof is difficult to implement, but it looks impressive.
Multi-gable roof
It is an original, complex architectural structure that can include a different number of slopes. Such a roof is most often installed in houses that have several levels, attics, attics, various extensions, etc. When installing a multi-gable roof, long sunken angles are formed between the slopes, called “gutters” or “valleys”.
The process of constructing a roof of this type is very labor-intensive and lengthy. When planning the construction of a multi-gable roof, you can realize even the most daring design ideas.
Advantages of a multi-gable roof
Disadvantages of a multi-gable roof
Spire roof
This roof option consists of a certain number of triangular-shaped slopes, connected at one point and mounted at an acute angle. Spire-shaped roofs are used in cases where the project involves the construction of towers. This roof is bright solution to create a unique look for the house under construction. Very often, such towers, if space allows, are used to arrange living rooms in them.

Roof spire diagram. All sides of the roof spire should be the same.
Advantages of a spire roof
Disadvantages of a spire roof
All options presented are considered fundamental. Each type can be well complemented with various details that can decorate the appearance of the house. But before choosing an acceptable option, it is necessary to take into account factors such as physical and climatic conditions, as well as the performance indicators that characterize the roof.
For areas with heavy snowfall, it is recommended to choose structures with a large slope angle; the roof will be protected from rapid damage, and the attics from leaks, which will extend the service life of the entire structure.
Main types of materials
Regardless of what type of roof is chosen, whether there are attics or not, the main role in reliability is played by the roofing and the material used for this purpose.
The main materials for reliable protection of a home from adverse weather conditions are:
According to the form of execution, roofing materials are divided into:
Roof made of various types materials have their advantages and disadvantages, so the choice depends on the desires of the developer and his capabilities.
Determining which roof and roofing is cheaper, as well as making a choice of roof design is a crucial moment, since the comfort of living and the duration of operation of the entire structure depend on this.
Which roof is best for a home?
 Which roof is best for country house
Which roof is best for country house
Main types of roofs
 Classification of pitched roofs
Classification of pitched roofs
Roof structural elements
Rafters and their types
Types of rafters:
 Types of rafters
Types of rafters
Roof bases
 Roofing materials
Roofing materials
Which roof is better and cheaper for a country house, cottage or cottage?
One of the most important parts of the house is the roof - its quality determines the warmth and comfort, noise level and frequency of repairs of the building.
Naturally, when planning a development, the question arises, what type of roof to choose, or which roof is better - cheaper, more expensive, broken or gable, or maybe hipped?
It is not enough for a roof to be simply durable and attractive. It must also have a number of important properties: provide good protection from rain and snow, protect from heat and cold, be fireproof. Let's look at the main types of roofs and their characteristic features, because the choice of roofing material depends on the type of roof.
Main types of roofs
Let us list the main structural types of pitched roofs.
Their surface is a plane resting on opposite walls of different heights, i.e. is at an angle to the horizontal.
They consist of two planes located at an angle and rest on opposite walls of the same height. This is perhaps the most common type of pitched roof.
A type of gable roof, in which each of the slopes consists of two located under obtuse angle rectangles.
They are a combination of several ordinary gable roofs, as if cut into each other at right angles.
These are hip roofs with two long trapezoidal slopes and two short triangular ones.
A type of hip roof, sometimes called a Dutch roof, in which the end slopes do not reach the eaves. Thanks to this design, the house is better able to withstand the wind, and its gables are less exposed to precipitation.
A type of 4-slope roof, consisting of four equal slopes of a triangular shape.
When choosing a roof type, you should take into account not only its intended operational properties, but also its decorative qualities. In low-rise buildings, the roof has a large relative volume and its appearance largely determines the architectural design.
In private houses, mainly the roofs of high structures are erected. This allows you to build an attic, and the house takes on a more presentable appearance. Also, steep slopes do not allow water and snow to linger on the roof. In areas with strong winds It is preferable to build low roofs or high ones, with additionally reinforced rafter systems.
You should also consider which roof the developer can afford. Naturally, the roofs are more simple designs cheaper, and the most economical options are flat and pitched roofing. An additional convenience of a pitched roof is that it allows you to increase the internal volume of the building, and in outbuildings at the same time serve as a ceiling.
If the attic space will be used for household needs, it is better to build gable roof. In areas with strong winds, the hip roof variety is the best choice, but it will be expensive to build. In addition, the construction hip roofs requires high professionalism, and should only be trusted by experienced craftsmen.
In houses of complex shape, cross-shaped roofs are usually used. This is enough complex design, consisting of many intersecting slopes. The difficulty of installing a cross-shaped roof is to ensure the tightness of the internal corners of the roof. Such roofs are expensive, they must be built experienced craftsmen and always made from quality materials.
Roof structural elements
After choosing the type of roof, you can begin selecting materials. Therefore, let's get acquainted with the main structural elements roofs:
Rafters and their types
The rafters perform important function in the roof structure. This is a support for the sheathing, taking on not only the weight of the roof, but also the wind load, as well as snow pressure.
Types of rafters:
The design and construction of rafter systems is work that requires great qualifications. Its quality determines bearing capacity and therefore the strength of the roof.
Roof bases
The type of base for the roof is selected depending on the intended roofing material.
There are two main types of roofing base:
Continuous flooring is constructed from two layers of boards. The first layer is called working, and the second – protective. The latter is located at an angle of 45 degrees relative to the worker and is constructed from narrow boards. Between these layers a windproof material is placed, usually roofing felt RRP-300 or 350.
When installing the sheathing, a number of rules are observed:
The top part of the roof is called the roof. It is in direct contact with the external environment, taking on the full power of wind and precipitation. Therefore, the main qualities that it must have are strength and water resistance.
There are many roofing materials, and when choosing one of them, you should take into account its performance characteristics, as well as a number of other factors:
It is difficult to give unambiguous and comprehensive advice on choosing which roofing material will be best, since it is influenced by all the listed factors, and ideal building materials, as we know, do not exist. In addition, the determining criteria may differ, for example, if there is insufficient funding, the price becomes the main thing, and all other factors are considered less meticulously. On the contrary, if consumer properties come to the fore, then price, as a rule, is not of decisive importance. For some, perhaps the main factor will be beauty or color, since according to the owners’ plans, the house should not be similar to the others.
The choice of material should be made at the stage of creating a house project, since the type of roof structure depends on it, and making changes to the finished project will be difficult and expensive.
Selecting a roof structure and roofing material is an important stage in building a house. The best solution can only be found by taking into account a number of factors:
Only by taking into account the listed factors and weighing each of them can you choose the optimal roof option and type of roofing material.
Which roof is better and cheaper for a country house, cottage or dacha - My Life

One of the most important parts of the house is the roof, because... the service life of the entire constructed building will depend on its strength and durability of the selected roofing material. That is why you need to be very careful when choosing a coating. For some, the most important question will be which roof is cheaper, while for others the aesthetic side of the roof or the price-quality ratio will be more important.
In order to decide on the choice of roof, you need to know the features and properties of different types of roofing coverings. The roof must have thermal insulation properties, provide protection from weather conditions and moisture, and maintain fire safety standards.
Roofs are divided into two types - pitched and flat.

Pitched roofs can be cold or warm, have an attic or not. In private construction, pitched attic roofs are usually used, because... This type of roof is easiest to convert to create additional living rooms or storage areas. Flat roofs are used for sheds, garages or other outbuildings. You can also make a roof in a residential building, on top of which you can arrange a comfortable terrace.
To choose the right type of roof for your home, you need to consider not only which roof is cheaper, but also the weather conditions in the area where the house is located.
It should be noted that for areas where there is heavy snowfall, a conventional gable roof would be an excellent solution, because... it removes sediment best. Flat roofs need to be installed in windy areas; they have little windage.

Mostly people prefer pitched roofs because... they allow the house to look more solid, proportional, and most importantly, it is possible to create an attic floor. To carry out such a roof, it is better to involve specialists, since this work is quite complex and requires a certain precision to ensure reliability. This type of roof will exert minimal pressure on the floors.

If the price-quality ratio is more important to you, then it is better to make a flat or pitched roof, because they are simpler and cheaper to install.
How the material will be used will depend on the roof design. However, it is worth saying that approximately the same amount of materials will be required to construct a gable and a shed roof, so it will be more difficult to say which roof is cheaper.

To begin choosing roofing materials, you should know the roof design. Its main components are:
1. The basis of the structure is beams, trusses and rafters;
2. Base – lathing or solid;
3. Insulation or insulator;
4. Roof covering.
Rafters and trusses are the main frame for the roof. They should be chosen carefully; this is best done by professionals. The rafters will take on the entire load and distribute it across the structures below: supports and walls. If you make a more massive and heavier rafter structure, then the entire frame will be more expensive than if it is made for a soft covering. The base for the roof is always made depending on the coating used. If soft or roll covering, then it is best to make a solid base.

If you use metal tiles or just tiles, you can also make a mesh base. Which coating is better, everyone will choose according to their needs: aesthetic appearance, durability and strength, waterproofness and thermal insulation, and most importantly - financial capabilities.
In light of financial possibilities, it is worth considering budget options. From this side, quality will be relegated to second place after cost.
When aesthetics are not a priority, you can use rolled polymer materials (for example, roofing membranes); they are excellent for flat roofs. Pitched roofs can also be covered with similar material, but only if the planks are secured on top. The basis for such a coating will be fiberglass to insulate sounds, moisture and heat.

More budget option is the coating of the roof slope with ondulin. Although it is susceptible to warping due to weather, it is still quite common.
After the previous options, it is worth mentioning corrugated sheets and metal tiles. The color options are huge. The accessories include everything needed to install the roof. The disadvantage of the material will be low noise insulation, for example, during rain. But this can be corrected if the backing is made of polyethylene foam.

It is also important to provide excellent thermal insulation of the roof to protect the entire building from temperature changes. In most cases, glass wool is used for insulation. The cheapest material today is polystyrene foam. However, it is very fragile and has low noise insulation. In this case, glass wool has several advantages, because it is not subject to combustion, the influence of temperatures, does not shrink or stretch.

Roof waterproofing can be easily done using vapor barrier film and non-woven polypropylene.
It is worth paying attention that it is better not to use too cheap materials for roofs, because... most often they are not the most environmentally friendly, and this will affect the health of the residents. But here it’s up to you: either choose which roof is cheaper or more environmentally friendly.
The roof must be reliable and solid. Otherwise, the entire structure will have a minimum service life.
Which roof is cheaper?
For many people, the name “flat roof” is associated primarily with multi-storey buildings. A flat roof - the pros and cons of which we will consider in this article - was practically not used in low-rise construction a dozen years ago. However, today creating such a roof in a country house is not a problem: modern materials and technologies make it possible to create a flat roof with appropriate consumer characteristics and at an affordable price.
Houses with flat roofs are very popular now
A flat roof, in addition to its advantages, has a number of disadvantages:
There are four types of flat roofs:

Flat roof base
In accordance with building codes, a flat roof, the pros and cons of which we discussed above, must have a base in the form of reinforced concrete floor slabs or corrugated sheets.
The durability of the roofing structure and its resistance to various negative influences depends on the use of special mixtures and technological processes for the production of roofing materials. Depending on the roofing materials, they are usually divided into three categories:

It is very important to properly waterproof your flat roof.
Whatever material is chosen, the joints between the rolls and the junctions with various roof elements must be waterproof. One of the main components of a successful waterproofing device is a high-quality sealant. During the period of operation, the roof is subject to negative influences external environment(moisture, hail, stones, strong temperature changes, etc.). Therefore, a high-quality sealant must be resistant to mechanical and temperature influences.
Mastic is usually used as a sealant - putty, which is based on elastic polyurethane resins. After application to the roof, the mastic polymerizes, resulting in the formation of a continuous rubber-like membrane that has waterproofing properties and protects the roofing from mechanical damage.
The mastic is ideal for flat roofs, is safe, has high adhesion to building surfaces, has high resistance to ultraviolet radiation, precipitation and all kinds of microorganisms. It is applied with a brush, roller or airless spray - in two multi-colored layers, which allows you to control the quality, layer thickness and uniformity of distribution of the sealant.
Regardless of the materials used, a flat roof must have a certain slope to drain water (usually within 3-5%) that appears on the roof as a result of precipitation. The drainage system should be thought out at the building design stage. Gutters determine how effectively moisture will be removed from the roof surface. To prevent gutters from freezing in winter, they are equipped with special thermal cables.

Drains can be organized, when both external and internal water supply is created, and unorganized. When creating an internal water supply system, the roof surface is divided into approximately equal parts of 150-200 square meters each. In places with a slope, drainage funnels are installed, equipped with baskets for catching debris. Typically, funnels are located in the center of the roof, and the pipes are located inside the building.

A flat roof needs insulation. In the absence of a layer of thermal insulation, condensation forms on the roof surface as a result of the contact of warm air masses and the cold surface of the roof. Condensation appears as water stains on the ceilings of the house, and the roof structure gradually collapses.
The roof design involves a base on which a layer of vapor barrier material is laid. The function of a vapor barrier is to protect the insulation from diffuse moisture coming from the premises of the building. The vapor barrier layer includes fiberglass reinforced membrane (based on bitumen and polymers) or vapor barrier film. The layer is laid on top of the screed, and along the edges of the roofing structure it is placed vertically to a height exceeding the height of the insulating material. The seams are sealed.

Insulation is placed above the vapor barrier layer, and a bitumen-based waterproofing carpet is placed on top of it. If expanded clay is used as insulation, then it is necessary to make a cement screed over it, then laying a couple of layers of waterproofing. If the roof is planned to be light (in the case where significant loads are not expected on it), then the waterproofing is simply glued along the entire perimeter of the roof.
For roofs without attics, both external and internal insulation methods are used. The external method is used more often, as its execution is simpler. There are two options for thermal insulation: double-layer and single-layer. The decision about which option to use in practice depends on heat engineering calculations and roof strength requirements. Thermal insulation slabs are placed on the roof structure based on the principle of “staggered seams”. With a two-layer coating of thermal insulation, the joints of the lower and upper slabs are also separated. In the area where the slabs adjoin the parapet, lanterns and walls, thermal insulating edges are created. Thermal insulation materials are attached to the base mechanically(screws, dowels), ballast (pebbles, paving slabs) or glue.
The roof structure must be equipped ventilation system. As a result of a violation of the tightness of the vapor barrier layer, moisture enters the insulating layer. A thick layer of waterproofing prevents evaporation from occurring, and moisture accumulates in the insulation. As a result, the material loses its insulation characteristics, and moisture appears on the ceilings of the building in the form of stains. In addition, water causes the waterproofing to swell, and at low temperatures, freezing water tears the waterproofing material away from the base. Temperature changes and mechanical damage contribute to the formation of cracks in the roof, which results in roof leaks.

To avoid these problems, the roof must “breathe”. For this, aerators are used - special devices in the form of plastic or metal pipes. They are covered with umbrella caps and are evenly distributed throughout the entire roof area, gravitating towards its highest points. The aeration mechanism works based on the principle of different pressures, which are created by air flows, removing excess moisture vapor from under the roof and preventing water bubbles from forming.
The installation of a roof is a responsible technological operation. Any, even minor, mistake in the design or construction of a roof can cause it to leak in the future. Therefore, when creating a roof, you need to pay attention Special attention correct selection hydro and thermal insulation materials, accurately calculate the upcoming loads on the roofing structure, and also select a team of competent builders.