
From the article you will learn:
One of the main parts of any plastic window is its transparent part, consisting of several glass sheets fastened to each other along the perimeter. Between the glasses there is an empty space filled with gas or rarefied air, and spacers are located along the edges of the glasses. A double-glazed window allows light to enter the room, as well as to see what is happening inside and outside.
In addition to providing access to daylight into the room, double-glazed windows perform several other important functions:
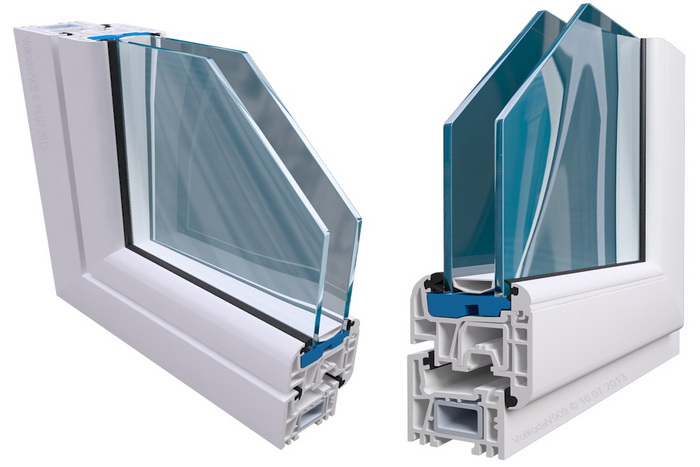
Any double-glazed window is a structure consisting of, separated by intervals of a given width and united by a plastic frame. Along the perimeter of the double-glazed window, spacers are laid between the glasses, which not only set the desired size of the gap, but also serve as a container for the granules of the absorbent mixture, designed to absorb excess moisture. For better absorption of moisture by the desiccant, there are dehydration holes in the spacers.
Reducing the window's permeability to loud sounds, moisture and air coming from the outside is provided by sealants. They are applied to the edges of the double-glazed window when gluing the sheets and before connecting the structure to the frame.

The empty space between the panes is filled with inert gases or air brought into a special state. Modern double-glazed windows are predominantly filled with gas, as it provides better insulating properties. The performance characteristics of a single-chamber double-glazed window filled with gas are better than those with ordinary air. The disadvantages of gas-filled double-glazed windows include the need for periodic "refueling" of their inert gas. Even the most thorough processing of the seams with a sealant does not save from the gradual weathering of the substance from the chambers of the double-glazed window.
I-glass
A thin layer of a low-emissivity metal coating is applied to the glass surface by spraying the composition in a vacuum electromagnetic field. The coating effectively reflects long waves of thermal radiation back into the room, keeping it warm. Each glass has an emitter index (E) - the amount of allowable heat loss. For ordinary glass, the coefficient E \u003d 0.83, and for energy-saving glass - no more than 0.04. Glasses with a soft low-emission sputtering retain heat inside 90% better than conventional products.
K-glass
A heat-saving layer of metal oxides is applied to a hot glass surface using the float method, forming a hard coating that is very durable and resistant to any damage. The characteristics of K-glass are slightly lower than those of analogues with a soft coating, but they are much stronger, do not lose their properties for a long time and are not afraid of contact with air and precipitation.